Contents
Get a Personalized Demo
See how Torq harnesses AI in your SOC to detect, prioritize, and respond to threats faster.
In today’s enterprise environment, raw data flows in from countless sources — often messy, fragmented, and incompatible. Effective data transformation is essential for turning this fragmented data into actionable, compliant, and secure intelligence.
With Torq’s AI Data Transformation, organizations can achieve seamless, scalable data workflows without writing code, dramatically enhancing security operations and compliance.
The Role of Data Transformation in Cybersecurity
What is Data Transformation?
Data transformation is the process of converting, cleaning, and manipulating raw data into a structured format that is suitable for analysis or other data processing tasks.
Data transformation is critical for:
- Data quality: Removing inconsistencies, duplicates, and errors.
- Data compatibility: Ensuring different systems and workflows can use the same data formats.
- Data reliability: Maintaining trust in analytics, compliance reporting, and operational decisions.
In a security context, data transformation keeps Hyperautomated workflows running smoothly by ensuring every downstream step receives data in the right format, at the right time. Without it, automation breaks, alerts go unprocessed, and compliance gaps widen.
How Data Transformation Works
- Data discovery: Identify and profile raw data sources to understand structure, quality, and required transformations.
- Data mapping: Define how fields will be transformed, matched, filtered, joined, and aggregated for the target system.
- Data extraction: Move data from source systems (structured or unstructured) to a staging or target environment.
- Code generation & execution: Use SQL, Python, or transformation tools to convert raw data into analytics-ready formats, running on a set schedule.
- Review: Validate transformation accuracy, completeness, and alignment with business requirements.
- Sending: Deliver transformed, structured data to its final destination, such as a data warehouse or analytics platform.
ETL and ELT in Data Transformation
In data engineering, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) are proven methodologies for shaping and preparing information. ETL transforms data before loading it into a data warehouse, while ELT loads raw data first and performs transformation inside the warehouse. Both approaches are designed to ensure clean, structured, and trustworthy data for analytics, reporting, and compliance.
Types of Data Transformation
The main types of data transformation used in security automation include:
- Aggregation: Summarizing multiple data points (e.g., calculating the average CVSS score).
- Anonymization: Obfuscating personal information to protect sensitive data, essential for compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Filtering: Selecting only the most relevant records (e.g., isolating high-severity vulnerabilities).
- Flattening: Converting nested or hierarchical data (such as JSON) into a flat, single-level table format so fields are directly accessible for querying, filtering, aggregation, and joining without complex parsing.
- Conditional Logic: Applying predefined rules to determine which data proceeds through the workflow.
- Data Cleansing: Removing invalid, duplicate, or incomplete data to improve accuracy.
- Data Enrichment: Enhancing records with intelligence from external threat feeds or authoritative databases.
Whether you’re extracting key attributes from JSON logs or merging disparate datasets, these transformation types ensure raw data becomes structured and usable intelligence.
How AI Data Transformation Accelerates Security and Compliance
AI data transformation automates complex processes such as converting formats, improving data integrity, and enhancing data observability. AI significantly speeds up compliance reporting, streamlines incident response, and provides richer, actionable data for security analytics.
Torq’s AI Data Transformation translates natural language into precise data commands, making these sophisticated tasks accessible to all users. Torq’s AI Data Transformation brings automation and intelligence to the process along with:
- Customizability: Edit or rewrite any command to suit your needs.
- Testability and reproducibility: Test transformations and validate results for precise control.
- Flexibility: Easily tweak transformations without disrupting your workflow.
- Visibility: See prompts, code, and results at every step — zero guesswork.
While other solutions leave you in the dark, using monolithic parsing that makes it challenging to edit or troubleshoot, Torq keeps you in control through micro-transformations. Every transformation in Torq is testable, customizable, and modifiable with just a click, ensuring your automation runs precisely as intended.
For security teams, this means faster threat enrichment, streamlined compliance reporting, and better data lineage tracking — all with built-in data privacy compliance.
Getting Started with Torq’s AI Data Transformation Operator
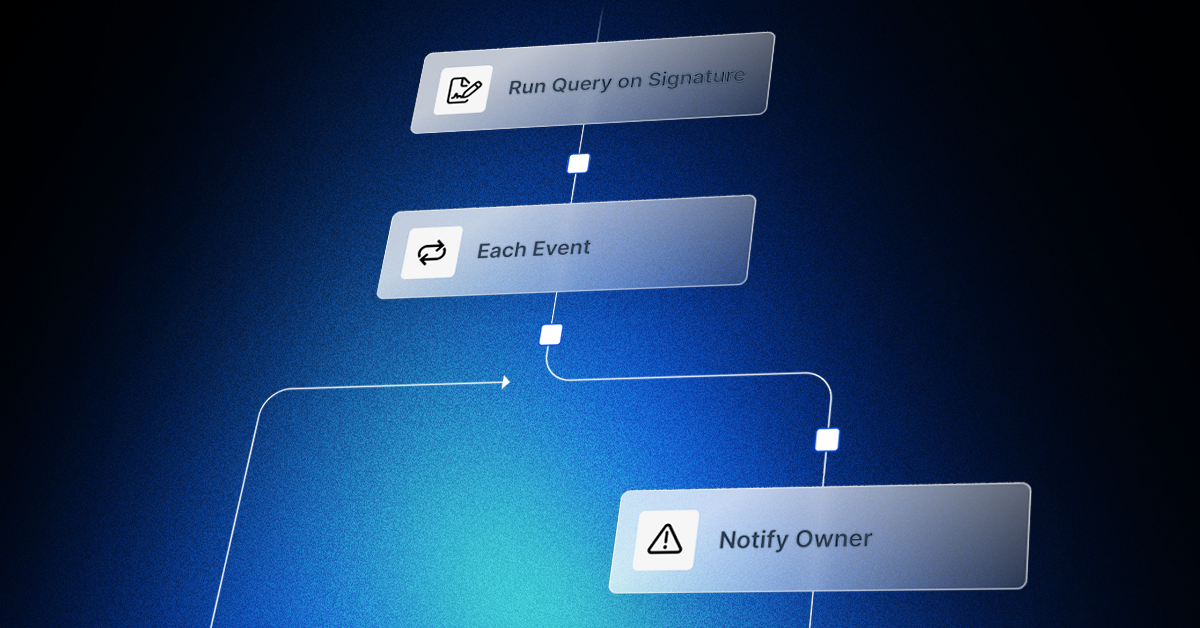
The Torq AI Data Transformation Operator is a workflow step that lets you manipulate JSON data inside Torq without needing deep programming skills. It combines AI-powered natural language prompts with deterministic JSON processing using JQ, a high-performance JSON transformation language. AI helps you write transformations in plain language, then Torq converts them into JQ commands that execute consistently.
How It Works
- Input your data: Pass JSON from a previous workflow step or paste it directly into the operator.
- Describe your transformation in plain language. For example:
- “Extract email, department, and action from each entry.”
- “Remove results where department is equal to Engineering.”
- “Group by department and count actions.”
- AI converts your prompt to JQ: The operator generates JQ code from your instructions. The AI step ends here; the deterministic JQ engine handles the actual execution.
- Chain multiple instructions: You can stack transformations — extraction, filtering, aggregation, string manipulation — all in one operator, with each step feeding into the next.
- Preview and adjust: See the output for each step before finalizing, and tweak the natural language instructions or the generated JQ directly.
- Save and reuse: If you create a transformation you’ll need often, you can save it as a custom step and reuse it across workflows or even share it across workspaces.
What You Can Do With It
The Data Transformation Operator supports a wide range of operations:
- Mapping and extraction (pull only the fields you care about)
- Renaming keys
- Converting data types
- Filtering and sorting
- Conditional logic (if/else rules)
- Math functions (averages, sums, etc.)
- String manipulation (splitting, regex)
- Restructuring JSON formats
Example Prompts
Need ideas? Here are a few natural language prompts and the associated JQ commands the Data Transformation operator could generate.
| Natural Language Prompt | AI Translated JQ Command | Security Impact |
|---|---|---|
| “Extract all high severity vulnerabilities” | .vulnerabilities[] | select(.severity == “high”) | Quickly prioritize critical security threats |
| “Group alerts by source IP” | group_by(.source_ip) | Identify potential attack patterns or compromised assets |
| “Calculate the average CVSS score” | [.[].cvss_score] | add / length | Assess the overall vulnerability landscape |
In security workflows, raw alerts and logs often come in messy, verbose JSON. The AI Data Transformation Operator lets you clean, normalize, and reformat that data on the fly, so the next steps in your workflow — whether enrichment, correlation, or reporting — get exactly the data they need in the right shape.
Torq Use Cases: Real-World AI Data Transformation in Security Operations
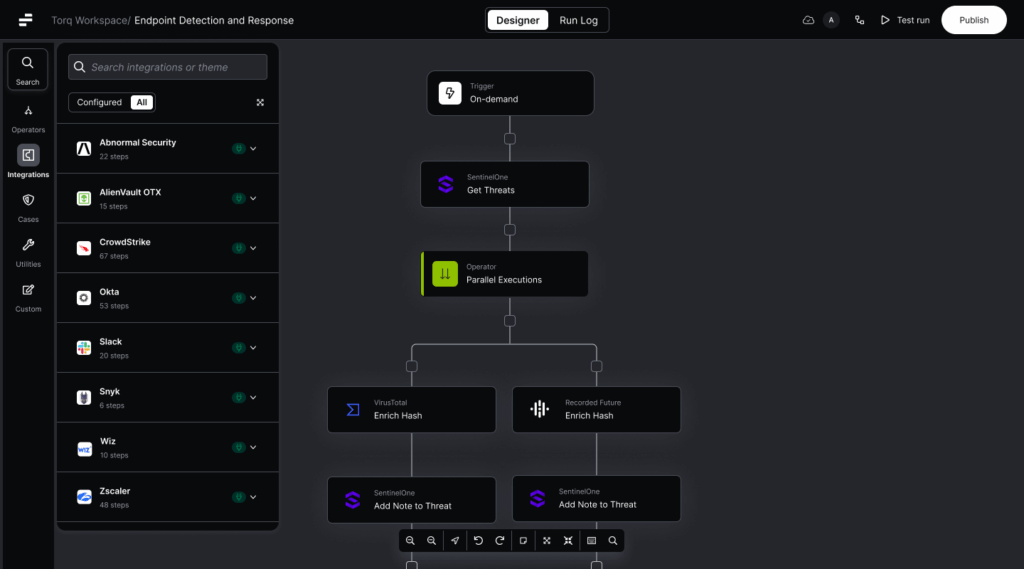
1. Normalizing SIEM Alerts Before AI Analysis
Challenge: SIEM alerts arrive in varied JSON formats depending on the source (cloud, endpoint, identity). Some include deeply nested keys or inconsistent field names.
Transformation:
- Extract only relevant fields (timestamp, src_ip, dst_ip, event_type, username).
- Rename fields for consistency (dst_ip → Destination IP).
- Convert timestamps into ISO 8601 for uniformity.
Outcome: Socrates, the AI SOC Analyst, receives a clean, uniform alert format for faster, more accurate triage.
2. Filtering Out Benign Events in EDR Logs
Challenge: EDR telemetry is high-volume, and not every event is actionable (e.g., routine system updates).
Transformation:
- Filter out entries where process_name equals known benign processes (e.g., svchost.exe in a non-suspicious path).
- Keep only events matching defined high-risk criteria (e.g., unsigned binaries, rare parent processes).
Outcome: Reduces noise before enrichment, allowing workflows to trigger only on meaningful events.
3. Aggregating Failed Login Attempts for Brute Force Detection
Challenge: IAM tools generate individual failed login events, making it hard to see patterns.
Transformation:
- Group events by username and source_ip.
- Count the number of failed attempts per user per IP within a set timeframe.
- Output only users exceeding a defined threshold.
Outcome: Aggregated insight triggers an automated account lockout or SOC escalation.
4. Enriching IOC Data Before Threat Hunting
Challenge: Incoming threat intelligence feeds may contain minimal metadata on indicators.
Transformation:
- Attach GeoIP data for IP addresses.
- Add WHOIS registration details for domains.
- Convert lists into an array of {indicator_type, value, source, risk_score} objects.
Outcome: Analysts and automation workflows have full context without additional lookups.
6. Preparing Audit Logs for Compliance Reporting
Challenge: Audit logs contain extra data that auditors don’t need, making reports bulky.
Transformation:
- Remove debug and low-value keys.
- Sort events chronologically.
- Output as a simplified JSON or CSV format matching compliance templates.
Outcome: Audit-ready reports generated instantly without manual editing.
These examples show how Torq’s AI Data Transformation Operator turns messy and inconsistent security data into clean, actionable intelligence that feeds directly into AI analysis, automation workflows, and case management.
Choosing the Right Data Transformation Tools and Software
Selecting the right data transformation software is critical for ensuring your workflows remain efficient, compliant, and adaptable as your organization’s needs evolve. When evaluating options, consider the following criteria:
- Ease of use and no-code or AI-driven functionality: Look for platforms offering intuitive interfaces and visual or AI-generated workflow builders so technical and non-technical users can wrangle complex data without writing scripts. This reduces engineering bottlenecks and speeds up deployment.
- Integration capabilities: Your data transformation tool should connect seamlessly with your existing security stack (SIEM, SOAR, EDR, threat intelligence feeds) and compliance systems (GRC, audit platforms). Native connectors and API support ensure smooth data integration across multiple environments.
- Scalability: As data volumes grow, especially in large enterprise and SOC environments, the platform must handle high-throughput processing without latency issues. Real-time or near-real-time transformation capabilities are essential for automation-driven incident response.
- Customizability and flexibility: Every organization has unique data mapping, aggregation, and enrichment needs. A robust platform allows you to tailor transformation logic, apply conditional rules, and reuse transformation templates without disrupting other workflows.
- Data governance and compliance support: Choose a solution that offers data lineage tracking, audit logs, and privacy controls to meet data privacy compliance regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific standards.
Why Torq Stands Out
Torq’s AI Data Transformation capabilities meet — and exceed — these criteria:
- No-code AI workflows: Transform complex JSON or other structured data using plain-language prompts automatically converted into precise JQ commands.
- Extensive integrations: 1,000+ prebuilt connectors for security, IT, and compliance tools.
- Enterprise-scale performance: Designed to handle large-scale, real-time data transformations without performance degradation.
- Full visibility and governance: Every transformation is testable, traceable, and compliant with your data governance policies.
Embrace AI-Driven Data Transformation
In a world where data flows faster and threats evolve by the minute, transforming raw, fragmented information into trusted, actionable intelligence is a competitive advantage. Torq’s AI Data Transformation delivers that capability, combining speed, compliance, and control in a no-code platform that works at enterprise scale. From unifying multi-source security alerts to streamlining compliance reporting, Torq ensures your workflows are reliable, transparent, and ready for whatever comes next.
See the difference for yourself. Request a personalized demo of Torq’s AI Data Transformation today and start turning your data into a decisive asset.
FAQs
Data transformation is the process of converting raw data from one format or structure into another to make it clean, consistent, and usable for analysis, storage, or automation. It typically involves tasks like data cleansing, mapping, aggregation, and enrichment.
AI data transformation uses artificial intelligence — often with natural language processing (NLP) — to automate these steps. Instead of manually writing scripts or queries, users can describe the desired transformation in plain language, and the AI generates the logic, executes it, and allows for easy customization. This speeds up the process, reduces technical barriers, and maintains accuracy and compliance.
A data warehouse stores structured, processed data in a consistent format, optimized for fast querying, analytics, and compliance reporting.
A data lake stores raw, unprocessed data — including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured formats — for flexible exploration, large-scale storage, and future processing.
Organizations often use both: the data lake for cost-effective retention of all data, and the data warehouse for ready-to-use insights that power day-to-day decision-making.
Data transformation is essential because it:
- Improves data quality by removing errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies.
- Ensures compatibility between different tools, systems, and formats.
- Supports compliance by enabling privacy controls, audit trails, and data lineage tracking.
- Enables better decisions by ensuring analytics, automation, and reporting run on reliable, well-structured data.
- Speeds up workflows by making data ready for automation and integration without manual intervention.
In security operations, data transformation ensures that alerts, logs, and intelligence feeds can flow seamlessly into detection, investigation, and response workflows.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Data is extracted from sources, transformed into the desired format, and then loaded into a data warehouse or destination system. This is ideal when you need consistent, cleaned data before it’s stored.
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): Data is extracted and loaded into the warehouse first, then transformed inside that environment. This approach is useful when storage is cheap and you want flexibility to transform data on demand.
Both approaches have their place, and modern AI data transformation tools like Torq can operate effectively in either ETL or ELT pipelines.
Common examples include:
- Format conversion: Converting XML to JSON.
- Data mapping: Aligning “src_ip” and “source_address” fields into a unified “source_ip” field.
- Filtering: Selecting only high-severity vulnerabilities from a dataset.
- Aggregation: Grouping alerts by source IP or calculating average CVSS scores.
- Enrichment: Adding threat intelligence data (e.g., IP reputation) to security alerts.
- Data cleansing: Removing duplicate log entries or fixing malformed timestamps